Content Delivery Network (CDN)
In today's fast-paced digital landscape, a Content Delivery Network (CDN) is essential for businesses striving to provide a smooth and efficient user experience—it's no longer just an option, but a necessity..
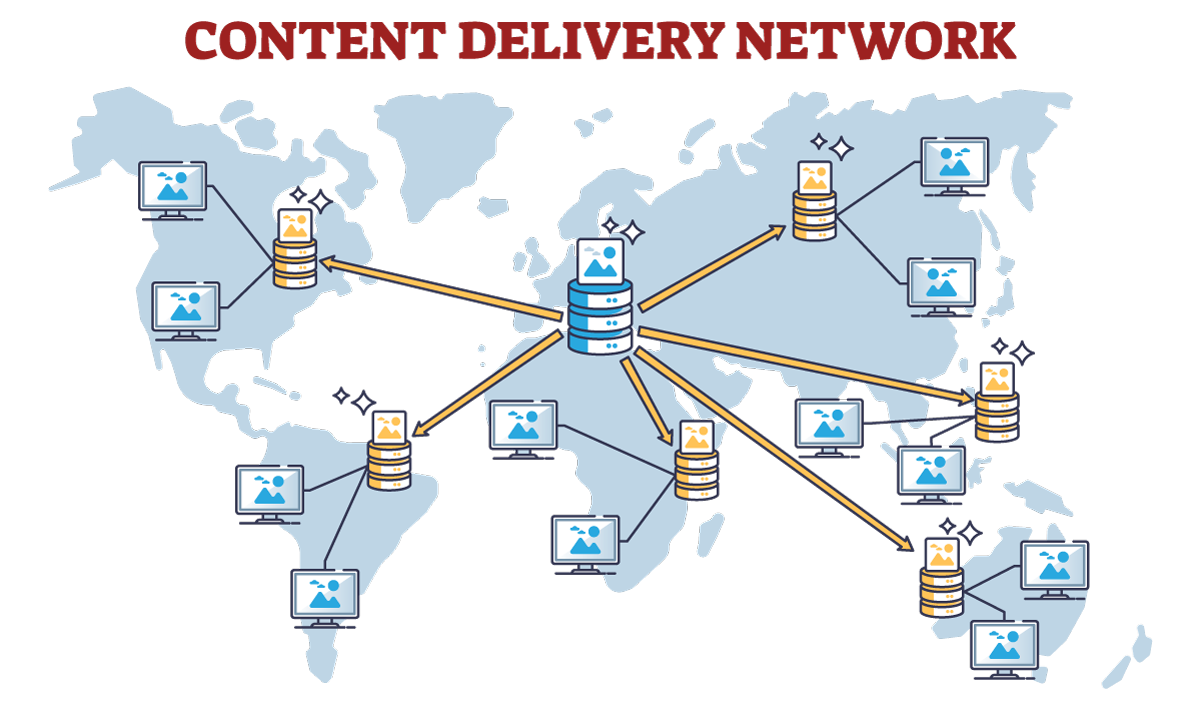
A CDN is a network of distributed servers that deliver content (web pages, images, videos, APIs) from the closest server to the user, reducing latency and improving performance.
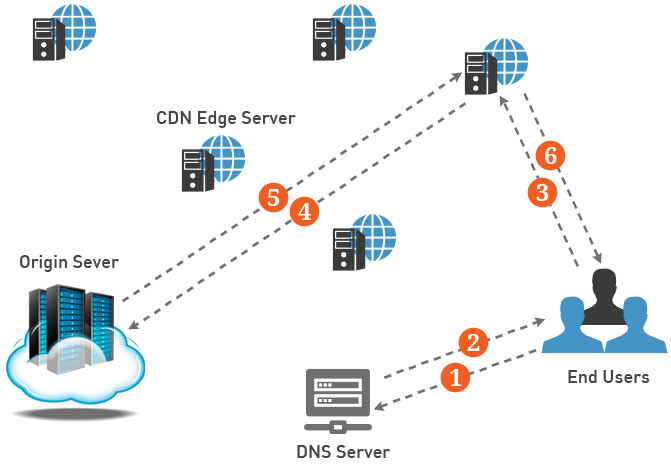
When a user visits a Web site, you first receive a response from the DNS server that contains the IP address of the host web server. Then your browser requests a web page content consisting of multiple static files such as HTML pages, CSS style sheets, JavaScript code and images which is served through the CDN.
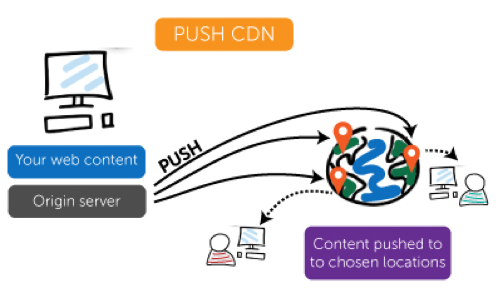
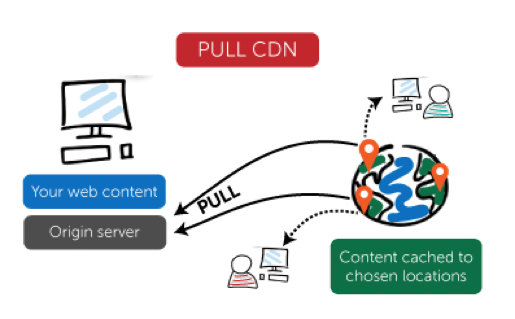
Many CDN supports custom domain so that you can create a CNAME record that points to the CDN endpoint in the following domains. The CDN routing requests to this endpoint (located much closer to the edge than the user's back-end server) The closest (Point of Presence) PoP user receives a user request. The PoP is configured with one or more of the CDN edge server deployment in Internet Exchange Points (IxP), a data center that is used to essentially Internet Service Provider (ISP) interconnect network. Then, the internal load balancer is one of the CDN edge server to route the request in the PoP and then provide content to users.
Faster Load Times – Users get content from nearby servers, reducing delays.
📈 Companies using CDNs see lower bounce rates, higher engagement. Whether you run an e-commerce site, a SaaS platform, or a media business, a CDN can be a game-changer.
Faster Load Times – Users get content from nearby servers, reducing delays.
CDNs aren’t just for speed—they’re essential for scalability, security, and better crawl rates. Whether you’re launching a stock photo site with 1M+ pages or ensuring a seamless user experience, CDNs are your ultimate ally.
Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a fast and efficient way to enhance a website's scalability and availability. By caching static assets across a globally distributed network, a CDN reduces latency and improves page load times for users. Additionally, it helps absorb user requests, minimizing bandwidth usage and lowering infrastructure costs through edge caching.